Sheikha Al-Mayassa bint Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani, the sister of Qatar’s absolute monarch Emir Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani, is well known for her love of art. The daughter of the country’s father, Emir Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani, – himself a notable art enthusiast – she has been declared the most influential person in art on Art+Auction’s top-10 list and ArtReview’s Power 100, and she has even appeared in the Forbes’ list of World’s 100 Most Powerful Women in 2014. Her plans to expand Qatar’s already impressive art and museum collection show no plans of slowing, with three new museums set to open soon, showing off Qatar’s culture to the world.
A prominent family name in the art collecting sphere
The 31 year-old is often called the Queen of the Art World, and as the chair of Qatar Museums and a prominent art collector, the title is well-deserved. She has overseen recent purchases of works by Damien Hirst, Andy Warhol, and Mark Rothko, as well as the record-setting purchase of Cezanne’s “The Card Players” for $250 million. In fact, it is said that Sheikha Al-Mayassa has nearly a billion euros to spend per year and has paid enormous sums for more than one major masterpiece.
Despite this, Sheikha Al-Mayassa did not actually study art, and instead she holds a double major in literature and political science from Duke University. Her prominence in the art world is not a surprise, however, as the Al-Thanii family, the absolute monarchy that rules the country, has several notable art collectors in its ranks. This includes her father, Sheikh Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani, former Emir of Qatar from 1995 to 2013 and current President of the Museum’s of Qatar, the most important institution for the culture and art in the country.
Qatar’s art is open to world
Sheikha Al-Mayassa is a firm believer that creative and cultural work is a driver of economic growth, and points to both the M7, Qatar’s epicenter for innovation and entrepreneurship in design, fashion and tech, and an exhibition with Al Jazeera for its 25th anniversary, which ‘put Qatar on the map 25 years ago’ as evidence of this.

Especially in the wake of the World Cup, which has seen the international community take more and more notice of the small gulf country, she has been keen to promote the artistic and cultural attractions of Qatar. She has said that, “We’re trying to show the diversity of the Arab world, but also we want people to experience Qatar as it really is,” and that, “there are interesting exhibitions about the Arab world that [were showcased for the very first time at the world cup].”
Among the various offerings are 18 public artwork installations, the Museum of Islamic Art, Mathaf: the Arab Museum of Modern Art, the Al-Riwaq gallery, Qatar National Museum, and more.
This list is only set to grow with the opening of three new major museums:
- The Art Mill, which will consist of a center with galleries exhibiting modern and contemporary art and that will run a program for resident artists, and whose construction will be under the control of Chilean architect Alejandro Aravena, a winner of the 2016 Pritzker Prize.
- The Lusail Museum, designed by the Herzog & Meuron architecture studio and which will house the world’s most extensive collection of oriental drawings, paintings, photographs, sculptures and texts.
- The Qatar Automobile Museum, an enormous 40,000m2 building that will showcase the history of the car from its invention to the present day. It will be the work of OMA, the architecture firm founded by Rem Koolhaas.
 Sheikha Al-Mayassa has said that their goal is to develop a cultural ecosystem in Qatar that encompasses museums, exhibition galleries, an ambitious public art program, schools, film, photography and performing arts festivals, events, spaces for emerging creatives and fashion professionals and of design. She said, “We know that culture and the creative industries are key drivers of economic growth, both in Qatar and globally. And another of our priorities, closely related to the development of a cultural ecosystem, is to help introduce Qatar to other nations and cultures and to welcome people from those countries. We encourage creativity and intercultural understanding.”
Sheikha Al-Mayassa has said that their goal is to develop a cultural ecosystem in Qatar that encompasses museums, exhibition galleries, an ambitious public art program, schools, film, photography and performing arts festivals, events, spaces for emerging creatives and fashion professionals and of design. She said, “We know that culture and the creative industries are key drivers of economic growth, both in Qatar and globally. And another of our priorities, closely related to the development of a cultural ecosystem, is to help introduce Qatar to other nations and cultures and to welcome people from those countries. We encourage creativity and intercultural understanding.”
Photos : graziamagazine.com – ft.com – tdg.ch


 North Field South is aiming to use the highest standards of extraction to reduce the greenhouse gas emissions associated with the project. The processing plant will be connected to Qatar’s electricity grid, meaning it will be powered in-part by renewable energy, mostly from the 800MW Al Kharsaah solar plant and the QatarEnergy solar plant currently under construction. Along with this, native CO
North Field South is aiming to use the highest standards of extraction to reduce the greenhouse gas emissions associated with the project. The processing plant will be connected to Qatar’s electricity grid, meaning it will be powered in-part by renewable energy, mostly from the 800MW Al Kharsaah solar plant and the QatarEnergy solar plant currently under construction. Along with this, native CO
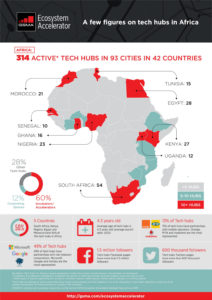 It is easy to conclude that the continent is already a hotbed for tech startups, especially as economic forecasts predict a record year for tech in Africa in 2022, with the possibility of total investments into startups reaching more than $7 billion. But while there is more money flowing into more companies than ever before, Africa’s record of scaling up these companies or even sustaining them, is poor.
It is easy to conclude that the continent is already a hotbed for tech startups, especially as economic forecasts predict a record year for tech in Africa in 2022, with the possibility of total investments into startups reaching more than $7 billion. But while there is more money flowing into more companies than ever before, Africa’s record of scaling up these companies or even sustaining them, is poor.


 The first major barrier for gas exports to Germany is the lack of infrastructure. Energy development projects are capital-intensive and generally require private-public partnerships. Sultan Wali, Ethiopia’s energy minister said that “African governments cannot carry out these projects alone.” Ndiarka Mbodji, the French-Senegalese founder of Berlin-based Kowry Energy echoed this, saying, “They need financial support from Germany and other rich western countries. Africa holds the key to resolving Europe’s energy crisis. And if we look at Africa’s resources, for example gas, you cannot underestimate its importance.”
The first major barrier for gas exports to Germany is the lack of infrastructure. Energy development projects are capital-intensive and generally require private-public partnerships. Sultan Wali, Ethiopia’s energy minister said that “African governments cannot carry out these projects alone.” Ndiarka Mbodji, the French-Senegalese founder of Berlin-based Kowry Energy echoed this, saying, “They need financial support from Germany and other rich western countries. Africa holds the key to resolving Europe’s energy crisis. And if we look at Africa’s resources, for example gas, you cannot underestimate its importance.” The
The 

 This aggregation of projects reduces the risk to investors, as well as the transaction costs of investing in multiple projects, and can help counter investment barriers that would prevent these projects from being financed. A recent report from the UNDP and Climate Bonds has shown that financial aggregation has untapped potential in bringing financing to small-scale clean energy projects. Eduardo Appleyard, CAP project coordinator says, “while the market is still nascent, financial aggregation could one day be a game-changer for distributed renewable energy companies…through this process we want to spark a conversation about financial aggregation grounded in real-life examples to help demonstrate its potential and better understand market barriers and opportunities.”
This aggregation of projects reduces the risk to investors, as well as the transaction costs of investing in multiple projects, and can help counter investment barriers that would prevent these projects from being financed. A recent report from the UNDP and Climate Bonds has shown that financial aggregation has untapped potential in bringing financing to small-scale clean energy projects. Eduardo Appleyard, CAP project coordinator says, “while the market is still nascent, financial aggregation could one day be a game-changer for distributed renewable energy companies…through this process we want to spark a conversation about financial aggregation grounded in real-life examples to help demonstrate its potential and better understand market barriers and opportunities.”

 AFEX Commodities Exchange Limited provides commodity brokerage services. The company has been developing a viable commodities exchange and supply chain infrastructure to support agricultural products since 2014, and it reached $31 million in revenue in 2020.
AFEX Commodities Exchange Limited provides commodity brokerage services. The company has been developing a viable commodities exchange and supply chain infrastructure to support agricultural products since 2014, and it reached $31 million in revenue in 2020.
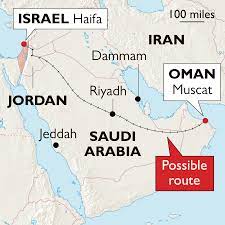 Benefits for everyone involved
Benefits for everyone involved