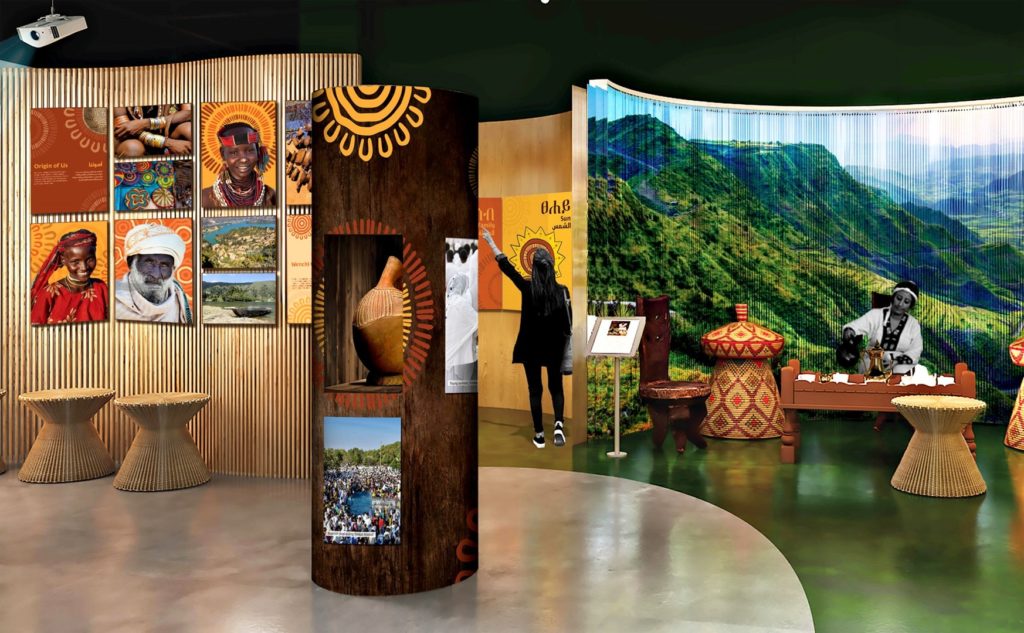
Turning towards a ‘circular economy,’ one that focuses on avoiding waste, promoting repair and reuse, and embedding ecological principles, is quickly gaining popularity in the world, but the transition to a circular economy will require policies, incentives, new infrastructure, and business support to make the change a reality.
The Covid-19 Pandemic has shrunk the economies of nearly every country in the world, which has led to renewed calls to restructure economies to support more resilient future growth. Turning towards a ‘circular economy,’ one that focuses on avoiding waste, promoting repair and reuse, and embedding ecological principles, is quickly gaining popularity in the developed world. In Africa these principles have always been practiced both consciously and unconsciously, and the continent is in a very strong position to take advantage of this. With support from local governments, industry, and the international community, Africa could leapfrog the developed world in embedding the principles of the circular economy into its industrial growth and infrastructure development projects.
The calls for a new economic system
The 20th century has been characterized primarily by the ‘linear’ economy, one that heavily relied on the “make, take, dispose” model. This has been hugely successful in industrialized nations and generated massive amounts of material wealth, however the extraction of resources has been highly unsustainable, and in the early 21st century it became increasingly clear that this type of consumption would have severe consequences for ecosystem quality, human health, and food and water prosperity. With the world’s population growing at rapid rates, the impacts are only going to become more severe, and the need for a more sustainable economic system is undeniable. The circular economy has gained traction over the years as an effective approach to achieve global, national, and local sustainability. The principles of mindful ecological practices, repair and re-use of items, and avoiding waste could be the solution to guaranteeing sufficient resources for future generations.
The Circular Economy exists informally in Africa
The idea of re-use, repair, and refurbishment of goods instead of disposing of them is practiced in Africa, but much of it exists at a startup or informal level. In Senegal a company called Proplast produces plastic resin from recycled plastic waste. In Kenya, Ecopost turns plastic into building materials. Despite the 5 million tons of plastic Ecopost has up-cycled so far, the country still produces far more plastic every year than the company can handle. Other industries are more developed though. The high cost of luxury goods like electronic equipment or cars is prohibitive to many people on the continent so cheaper options must be found. In Nigeria, 95% of cars are second-hand vehicles, and in Ghana 80% of second-hand electronic products are re-used, repaired, or refurbished.
Challenges to the circular economy in Africa
The circular economy in Africa is mostly practiced at a small or informal level, but if the benefits are to be properly realized, a coordinated, strategic approach will be necessary. If this does not happen, there is the risk that companies will adopt token or even harmful activities under the name of ‘circularity.’ This could ultimately lead to even worse results, for example waste-to-energy initiatives could see sub-standard burning practices employed that create health risks. In Agbogbloshie, Ghana, it is common to burn insulated copper wire. Once the plastic insulation is gone, the copper wire can be easily recycled for trade, however this process exposes workers to dangerous levels of carbon monoxide and other hazardous chemicals. Likewise, recycling initiatives with poor practices could see ‘pickers’ risking physical harm in landfill sites – a practice that is already common in much of the developing world.
At the other end of the spectrum, switching to circular solutions would lead to large-scale shifts in industrial policy and this could risk job losses for those employed in resource extraction and processing. Careful consideration and management of these problems will be required in order to see a successful transition to a more sustainable economic system.
Making the circular economy a success for the continent
In a report by the World Economic Forum’s Circular Economy initiative titled “5 Big Bets for the Circular Economy in Africa,” the waste conversion, plastic waste recycling, e-waste recycling, mass timber, and garment recycling industries are identified as the sectors that can lead the charge towards a sustainable, circular economy on the continent. Training farmers to recover irrigation wastewater and converting food waste into organic fertilizer, instigating bottle deposit systems, conserving forests, and developing the e-waste repair and recycling capacity of nations can bring new opportunities and resilience to Africa’s economic sector. But these are not overnight projects, and the transition to a circular economy will require policies, incentives, new infrastructure, and business support to make the change a reality.
Photo : iucn.org






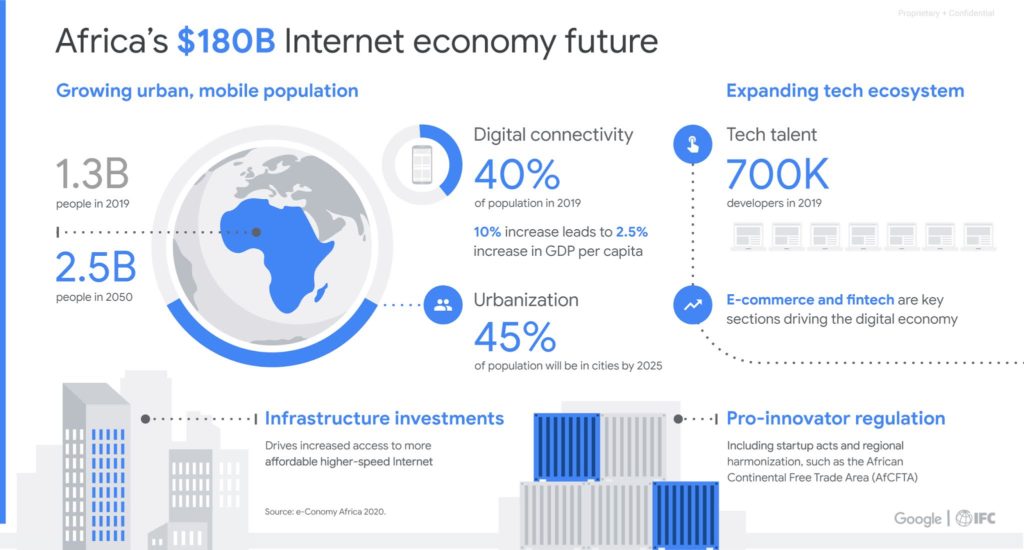
 ADCA’s report, while positive about the future growth prospects of internet in Africa, did warn that achieving the 700 data center target would be challenging. The land, power, and water requirements for data centers of a meaningful scale would need national, regional, and local government involvement. It also would come with a high cost. The average yearly cost to operate a large data center ranges from $10 to $25 million, before taking into account the upfront costs of building the data center and the initial set-up. When including access, power, network connections, servers, storage units, and software licenses the cost can be significant. One mile of fiber-optic connections alone can cost as much as $250,000. To make things more difficult, the infrastructure supply chain in Africa is significantly less developed than in Europe, Asia or the USA and many important components will have to be brought in from overseas.
ADCA’s report, while positive about the future growth prospects of internet in Africa, did warn that achieving the 700 data center target would be challenging. The land, power, and water requirements for data centers of a meaningful scale would need national, regional, and local government involvement. It also would come with a high cost. The average yearly cost to operate a large data center ranges from $10 to $25 million, before taking into account the upfront costs of building the data center and the initial set-up. When including access, power, network connections, servers, storage units, and software licenses the cost can be significant. One mile of fiber-optic connections alone can cost as much as $250,000. To make things more difficult, the infrastructure supply chain in Africa is significantly less developed than in Europe, Asia or the USA and many important components will have to be brought in from overseas.