The e-Conomy Africa 2020 report, a unique collaboration between the IFC and Google, sheds light on the great potential of Africa’s Internet economy, the promising tech entrepreneurs driving innovation, and the growing tech talent across the continent.

The e-Conomy Africa 2020 report, a unique collaboration between the IFC and Google, sheds light on the great potential of Africa’s Internet economy, the promising tech entrepreneurs driving innovation, and the growing tech talent across the continent. Of the top 20 fastest-growing countries in the world, nineteen are located in Africa. Driven by greater access to the internet as well as having an increasingly young and well-educated workforce, the IFC and Google predict an internet economy on the African continent worth $180 billion by the year 2025. This could reach $712 billion by 2050 and despite the impact of Covid-19, this ‘e-conomy’ is expected to be more resilient to the pandemic. This offers several promising avenues for investment on the continent.
Sectors Driving the Growth of the Internet Economy in Africa
Thanks in large part to easier access to mobile internet, several key sectors have been able to flourish in recent years:
- Fintech, or financial technology, enjoys an average of 120% growth in funding year-on-year, and is the most heavily funded sector in Africa. With large amounts of the population unbanked, startups allow people to leapfrog from physical retail banking to online banking by offering services like payment processing, personal finance, insurance and microloans. Companies like M-PESA in Kenya, Fawry in Egypt and Paystack-62 in Nigeria lead the way in, with some companies growing at more than 100% annually.
- Healthtech received $189 million in 2019, and the healthcare market in Africa is expected to reach over $100 billion by 2030. Companies like Zipline have been operating medical supply drone deliveries to rural areas, while Helium Health has been providing technological solutions for healthcare providers.
- Media and Entertainment has seen a rapid increase in demand, thanks in part due to lockdowns and social distancing measures put in place to prevent the spread of Covid-19. Content specifically created in Africa can be found on globally-available streaming platforms, such as Netflix’s “Made in Africa” collection, and African-made content is expected to expand quickly.
- E-Mobility and Food Delivery has been hard hit by the pandemic, as ride-hailing saw a decrease in demand due to work-from-home and lockdown measures. It is expected to rebound quickly however, as Africa has one of the lowest car to person ratios in the world. In some areas taxis and moto-taxis make up nearly 80% of motorized trips. Global ride-hailing companies like Uber and Bolt have entered the market in the past seven years, in addition to local startups, such as Little, Gokada, Gozem, MaxNG, Safeboda and Yassir. Startups within the e-mobility sector in Africa raised $62 million in 2019. Many of these startups have branched into food and grocery delivery to alleviate the impact of Covid-19.
- E-Logistics platforms are helping informal retailers with companies such as Kobo360, Lori Systems, Sendy, and Truckr reducing the cost of cargo and local transportation.
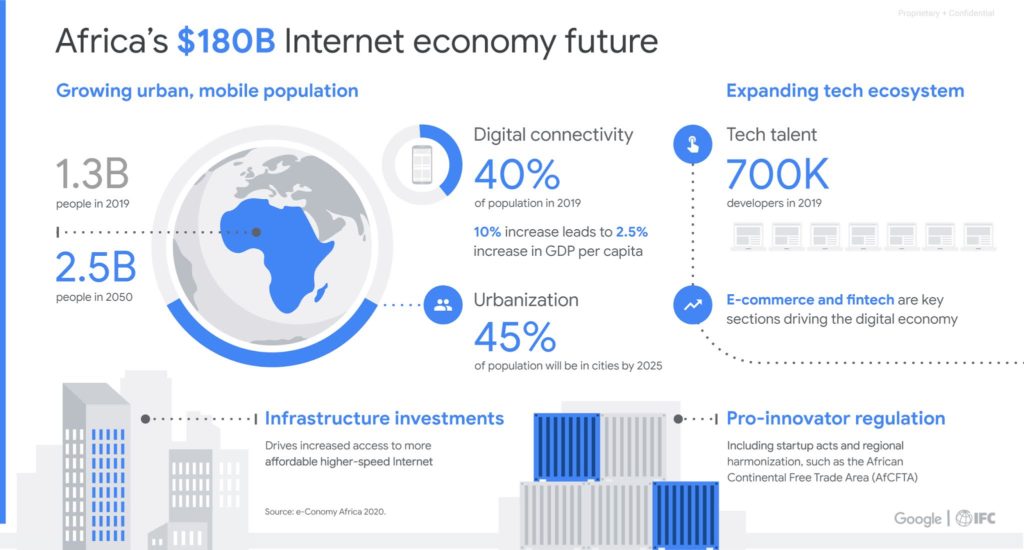
Young Tech Talent in Africa Drives the Growth and Consumption of Online Services
Africa has the world’s youngest and fastest-growing workforce, one that is increasingly urbanized. Tech talent in Africa is at a historical high with nearly 700,000 professional developers across Africa, a number that is still rising. Women comprise one in five of the total developer population in Africa, higher than the United States, creating new opportunities for women, especially in Egypt, Morocco and South Africa. A skills gap still exists, with self-taught developers making up the same number of as those that are university-trained. Helping to bridge this gap will help encourage the growth of the internet economy in Africa.
With support and regulation from regional governments, the internet economy in Africa looks set to boom in the coming years, thanks to the hard work and entrepreneurship of local startups on the continent.
Photos : ifc.org – bp.blogspot.com – miro.medium.com















